If you’re a student of physics or a researcher in the field, you know the importance of accuracy in your measurements. And, with that comes the need to understand how to calculate percentage error physics. It’s a crucial concept that can make or break your data. So, let’s dive into the details of how to calculate percentage error physics in this comprehensive guide.
Pain Points with How to Calculate Percentage Error Physics
As we all know, physics is a complex field of study that requires accuracy and perfection. One small mistake in your measurements can lead to incorrect results and jeopardize your entire project. Understanding how to calculate percentage error physics is a crucial step in ensuring that your experiments are accurate and reproducible. However, many students struggle with this concept, leaving them frustrated and demotivated.
Answering the Question: How to Calculate Percentage Error Physics
Before we dig deeper into the topic, let’s first understand what percentage error is. A percentage error is the difference between the actual value and the measured value, expressed as a percentage of the actual value. To calculate percentage error in physics, we use the following formula:
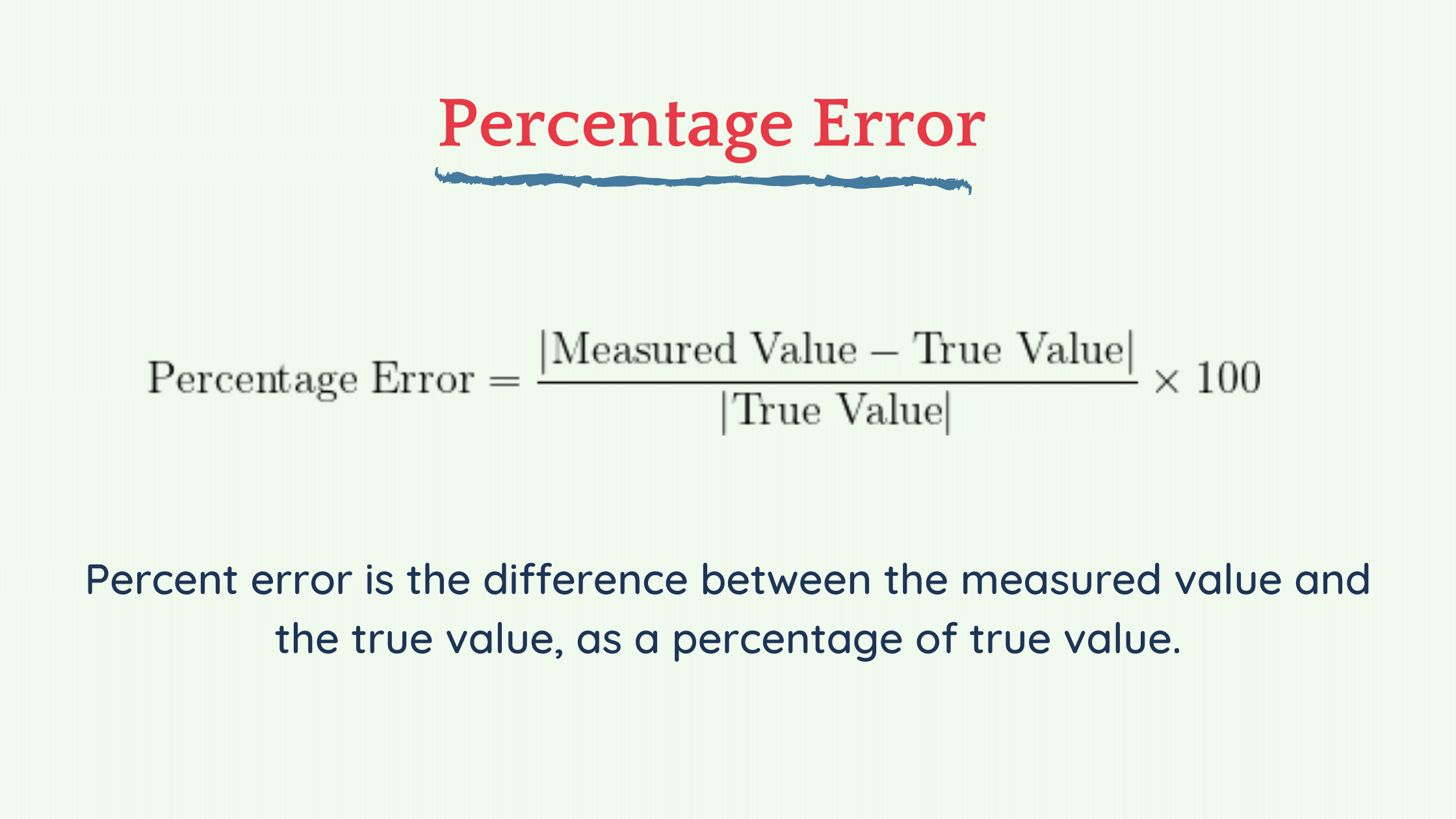
The above formula can be used to calculate the percentage error for any experiment or measurement in physics. It’s important to note that the measured value is always subtracted from the actual value, as we are interested in finding out the deviation of the measured value from the actual value.
Summary of Main Points Related to How to Calculate Percentage Error Physics
In summary, calculating percentage error physics is a crucial step in ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of experiments. It’s a simple formula that can be used for any kind of measurement in physics. By understanding and implementing this formula correctly, you can avoid errors and ensure that your research is successful.
How to Calculate Percentage Error Physics: Personal Experience and Explanation
When I was a student of physics, I struggled with the concept of percentage error. I would often get confused with the formula and end up with incorrect results. However, with time and practice, I was able to grasp the concept and apply it successfully in my experiments.
Let’s take an example to understand how to calculate percentage error physics in detail. Suppose you have to measure the length of a wire using a ruler. The actual length of the wire is 20 cm, but you measure it to be 18 cm. To calculate the percentage error, we will use the formula:

Using the above formula, we get:
Percentage Error = ((20 – 18) / 20) x 100% = 10%
So, the percentage error in this case is 10%. This means that the measured value is 10% less accurate than the actual value. By using the percentage error formula, we can easily calculate the deviation of our measurements from the actual value.
How to Calculate Percentage Error Physics: Importance and Applications
Calculating percentage error is a crucial step in various fields of science, including physics. It helps us understand the level of accuracy of our measurements and makes sure that our experiments are reproducible. It’s used extensively in research and experiments where precision and accuracy are critical, such as in the study of physical constants, temperature measurements, and more.
Additionally, calculating percentage error can also help us identify faulty equipment or measurement techniques. If we consistently get high percentage errors in our experiments, it’s an indication that something is wrong with the setup, and we need to troubleshoot it.
Frequently Asked Questions about How to Calculate Percentage Error Physics
Here are some common questions related to how to calculate percentage error physics:
Q: What is the difference between accuracy and precision?
A: Accuracy refers to how close the measured value is to the actual value. Precision, on the other hand, refers to how consistent the measurements are. A measurement can be precise, but not accurate, and vice versa.
Q: Can the percentage error be negative?
A: Yes, the percentage error can be negative if the measured value is greater than the actual value. However, it’s usually expressed as a positive value.
Q: How can I reduce the percentage error in my experiments?
A: You can reduce the percentage error in your experiments by using more precise equipment, improving your measurement technique, or taking multiple measurements and averaging the values. It’s also important to be aware of any sources of error in your experiment and try to minimize them.
Q: Is percentage error the same as relative error?
A: Yes, percentage error is the same as relative error and can be expressed in the form of a percentage.
Conclusion of How to Calculate Percentage Error Physics
Calculating percentage error physics is a crucial step in ensuring the accuracy and reproducibility of experiments. It’s a simple formula that can be used for any kind of measurement in physics. By understanding and implementing this formula correctly, you can avoid errors and ensure that your research is successful.
Gallery
How To Calculate Percent Error Equation

Photo Credit by: bing.com / physics
Percent Error Formula Calculator – New Page 1 Www.pstcc.edu : To
Photo Credit by: bing.com / percentage calculate vls riich difference equation
How To Calculate Percentage Error – Definition, Formula, And Examples

Photo Credit by: bing.com / error percentage calculate definition formula errors examples define
How To Calculate Percent Error?- Concept And Calculation, Meaning
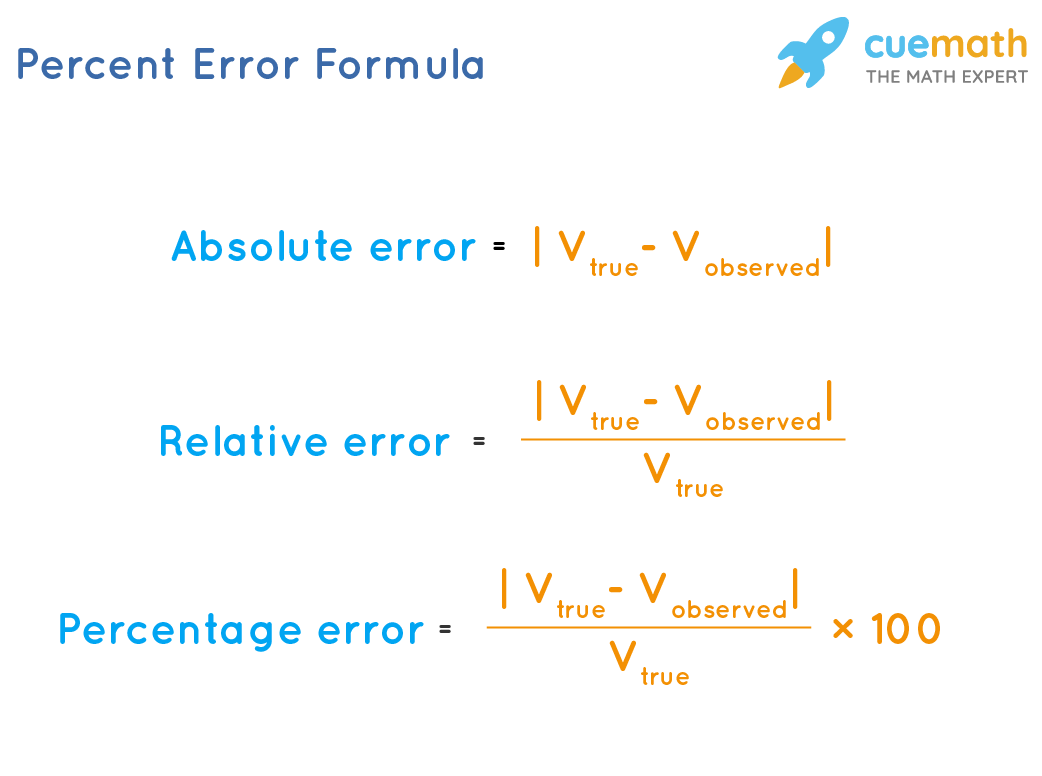
Photo Credit by: bing.com / absolute calculate calculation
How To Calculate Percentage Error In Physics – Tutordale.com

Photo Credit by: bing.com /